Identification of molecular basis for aggressive malignancies and drug resistance of renal cancer
Research Press Release | February 24, 2016
|
Key Points |
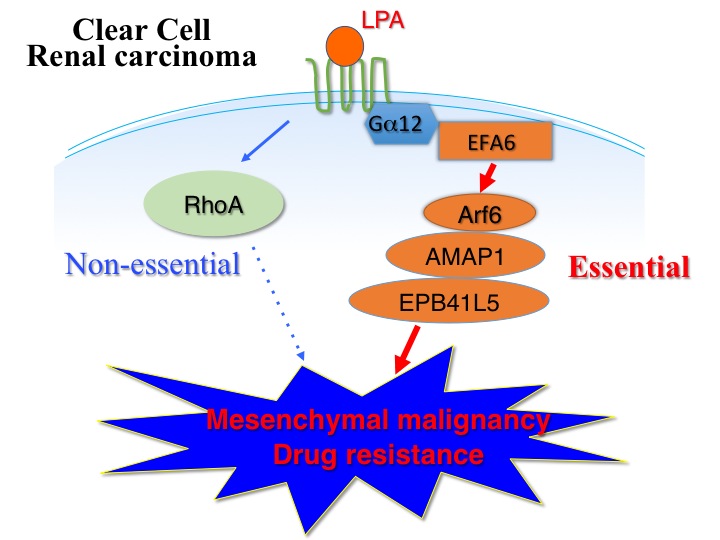
・A major factor promoting malignancies of clear cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCCs) is a lipid mediator, lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). ・LPA activates a small GTPase Arf6 and hence promotes mesenchymal malignancies and drug resistance. ・This Arf6 pathway includes a mesenchymal-specific protein that is not expressed in non-metastatic cancers. ・Blockade of the Arf6 pathway suppresses the mesenchymal malignancies and drug resistance. ・High levels of the mesenchymal-specific protein of this pathway provides a clear biomarker to identify treatable ccRCCs. |
|
|
Outline |
Clear cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCCs) account for 70% to 80% of the kidney cancers. ccRCCs are often highly resistant to therapeutic drugs and ionizing radiation, and exhibit recurrence with a rate of 30-40% of the patients. Onset of the mesenchymal programs of ccRCCs has been highly implicated in their advanced malignancies, including invasiveness and high metastatic abilities. Scientists at Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine now reports that a lipid mediator lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is the major factor that promotes mesenchymal malignancies of a large population of primary ccRCCs, together with fine molecular mechanisms therein involved. LPA is well known to activate a small GTPase Rho, and has long been believed to thereby promote cancer malignancies. The research team led by Professor Hisataka Sabe have clarified that LPA activates another small GTPase, Arf6, in ccRCCs; and that Arf6 then needs a mesenchymal-specific protein EPB41L5, which is not normally expressed in epithelial cells, to promote invasion, metastasis and drug resistance. They have moreover demonstrated that RhoA activity is dispensable in these processes of the cancer malignancies. Analyses on pathology specimens reveal that high levels of expression of the Arf6-based pathway components, especially EPB41L5, exhibits statistical, tight correlations with poor overall survival of the patients. The kidneys are natural filers of body fluids, while, on the other hand, LPA can be produced easily in body fluids by an extracellular enzyme autotaxin. Thus, these results identified mechanisms as to how aggressive malignancies, as well as robust resistance to therapeutics, arise in many primary ccRCCs in response to a component of the body fluids. Since this research team has previously reported several methods that effectively causes blockade of Arf6 and its signaling pathway, these findings will provide excellent therapeutic opportunities toward many ccRCC patients. Shigeru Hashimoto, a Specially Appointed Associate Professor of Hokkaido University, played a key role in this study. This study was performed in a collaboration with researchers of Keio University School of Medicine, Professor Mototsugu Oya and Senior Assistant Professor Shuji Mikami. |
|
| Inquiries |
Hisataka SABE, Professor Department of Molecular Biology, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine sabeh[at]med.hokudai.ac.jp |
|
|
Japanese Link |
腎明細胞癌の浸潤・転移性並びに薬剤耐性の分子基盤の解明 (02.09.2016) | |
|
Publications |
Lysophosphatidic acid activates Arf6 to promote the mesenchymal malignancy of renal cancer, Nature Communications (02.08.2016) | |
