The Antiarrhythmic Agent Verapamil Improves the Therapeutic Effect of the Anticancer Drug Paclitaxel by Inhibiting the Transporter in Tumor Blood Vessels
Research Press Release | January 22, 2015
-
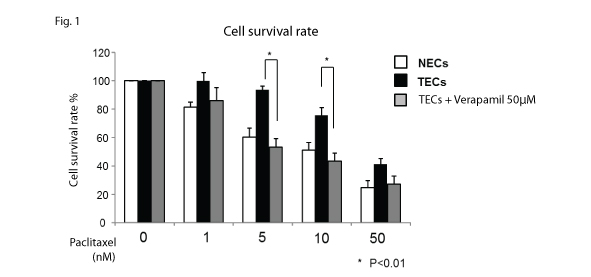 Fig. 1
Fig. 1 -
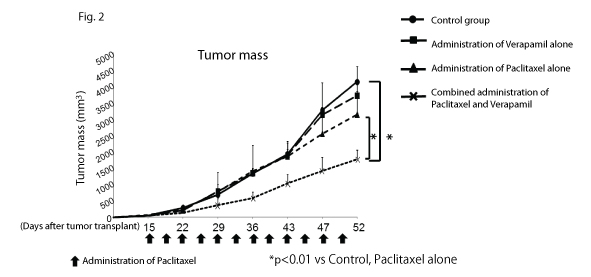 Fig. 2
Fig. 2 -
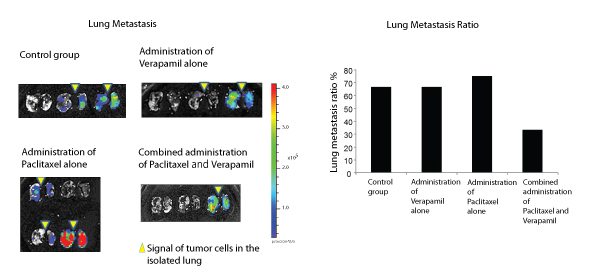
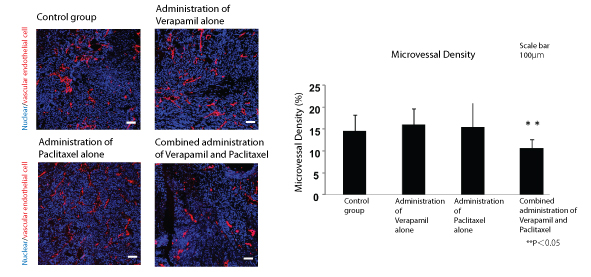 Fig. 2(1)
Fig. 2(1)
Fig. 2(2)
| Press Release | ||
|---|---|---|
| Key Points |
・The antiarrhythmic agent verapamil was found to inhibit the drug resistance in tumor blood vessel cells. (Tumor Endothelial Cells: TECs). ・Verapamil improves the anti-cancer effect of Paclitaxel by inhibiting the transporter in TECs. ・Combination therapy with verapamil and the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel enhanced the inhibitory effects on tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. ・The possibility of expanded applications of existing drugs for cancer therapy which target tumor blood vessels was demonstrated. |
|
| Overview |
Recently, Researcher Kosuke Akiyama, Project Associate Professor Kyoko Hida and others reported that the resistance to anticancer drugs is present not only in cancer cells, but also in tumor endothelial cells (TECs)1). In this study, it was found that by inhibiting ABC transporter2) in TECs, the antiarrhythmic agent verapamil inhibits TEC’s resistance to the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel3), and as a result, improving its therapeutic effect. In therapy experiments using mice, a combination of verapamil and a low dose of the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel4) was found to provide anti-tumor and inhibitory effects on cancer metastasis that could not be obtained with paclitaxel alone. The discovery that these results were attributable to anti-angiogenetic effects is a first in the world. 1) Tumor Endothelial Cells: TEC Thin, flat cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels are called vascular endothelial cells. In comparison with the endothelial cells in normal blood vessels, TECs lining the blood vessels in tumor tissues are reported to have molecular-biologically different characteristics such as the acceleration of specific gene expressions. 2) ABC Transporter A membrane transporter which transports substances using ATP energy. P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is well-known as a drug-resistant related molecular transporter, and functions to discharge specific drugs from inside the cell to outside the cell. In cancer cells, its correlation between p-gp upregulation and drug-resistance has been reported. 3) Paclitaxel An anti-cancer agent belong to the taxane family. Paclitaxel inhibits cancer cell division by bonding to cell microtubule and stabilizing it, and inhibiting depolymerization. 4) Verapamil A calcium channel inhibitor to control the aperture of the membrane calcium channel. It is generally used as an anti-arrhythmic drug. Moreover, it is known as inhibitor to block P-gp function. |
|
| Inquiries |
Kyoko Hida, Specially Appointed Associate Professor, Institute for Genetic Medicine, Hokkaido University TEL: +81-11-706-4315 FAX: +81-11-706-4325 E-mail: khida@igm.hokudai.ac.jp |
|
|
Japanese Link |
抗不整脈薬ベラパミルはがん血管のトランスポーターを阻害することで抗がん剤パクリタキセルの治療効果を高める | |
| Publications | Inhibition of Multidrug Transporter in Tumor Endothelial Cells Enhances Antiangiogenic Effects of Low-Dose Metronomic Paclitaxel (The American Journal of Pathology, 2014.12.8) | |