Emerging infectious disease caused by a new nairovirus identified in Japan
Research Press Release | October 04, 2021
A previously unknown virus that can infect humans and cause disease has been identified by scientists in Japan. The novel infectious virus, named Yezo virus and transmitted by tick bites, causes a disease characterized by fever and a reduction in blood platelets and leucocytes. The discovery was made by researchers at Hokkaido University and colleagues, and the results have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
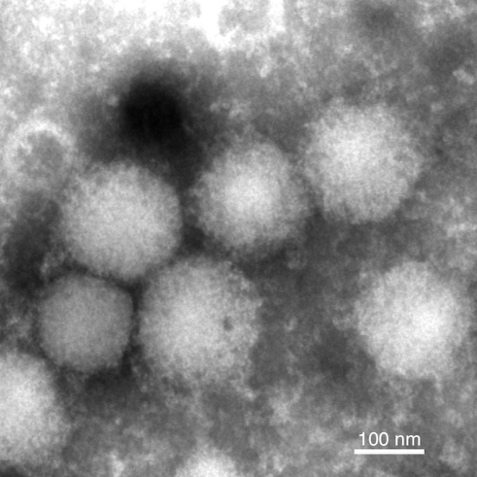
The study suggests that the Yezo virus, a type of orthonairovirus, transmits between animals and humans via ticks and causes fever and other symptoms in humans. (Fumihiro Kodama, et al., Nature Communications, September 20, 2021)
Keita Matsuno, a virologist at Hokkaido University’s International Institute for Zoonosis Control, said: “At least seven people have been infected with this new virus in Japan since 2014, but, so far, no deaths have been confirmed.”
The Yezo virus was discovered after a 41-year-old man was admitted to the hospital in 2019 with fever and leg pain after being bitten by an arthropod believed to be a tick while he was walking in a local forest in Hokkaido. He was treated and discharged after two weeks, but tests showed he had not been infected with any known viruses carried by ticks in the region. A second patient showed up with similar symptoms after a tick bite the following year.
Genetic analysis of viruses isolated from blood samples of the two patients found a new type of orthonairovirus, a class of nairovirus, that includes pathogens such as the Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus. The scientists named it Yezo virus, after a historical Japanese name for Hokkaido, a large island in the north of the country where the virus was discovered. The novel virus was found most closely related to Sulina virus and Tamdy virus, detected in Romania and Uzbekistan, respectively, the latter of which reportedly caused acute fever in humans recently in China.
The scientists then checked blood samples collected from hospital patients who showed similar symptoms after tick bites since 2014. They found additional positive samples from five patients. These patients, including the first two, had a fever and reduced blood platelets and leucocytes, and showed indicators of abnormal liver function.
To determine the likely source of the virus, the research team screened samples collected from wild animals in the area between 2010 and 2020. They found antibodies for the virus in Hokkaido shika deer and raccoons. They also found the virus RNA in three major species of ticks in Hokkaido. Matsuno says, “The Yezo virus seems to have established its distribution in Hokkaido, and it is highly likely that the virus causes the illness when it is transmitted to humans from animals via ticks.”
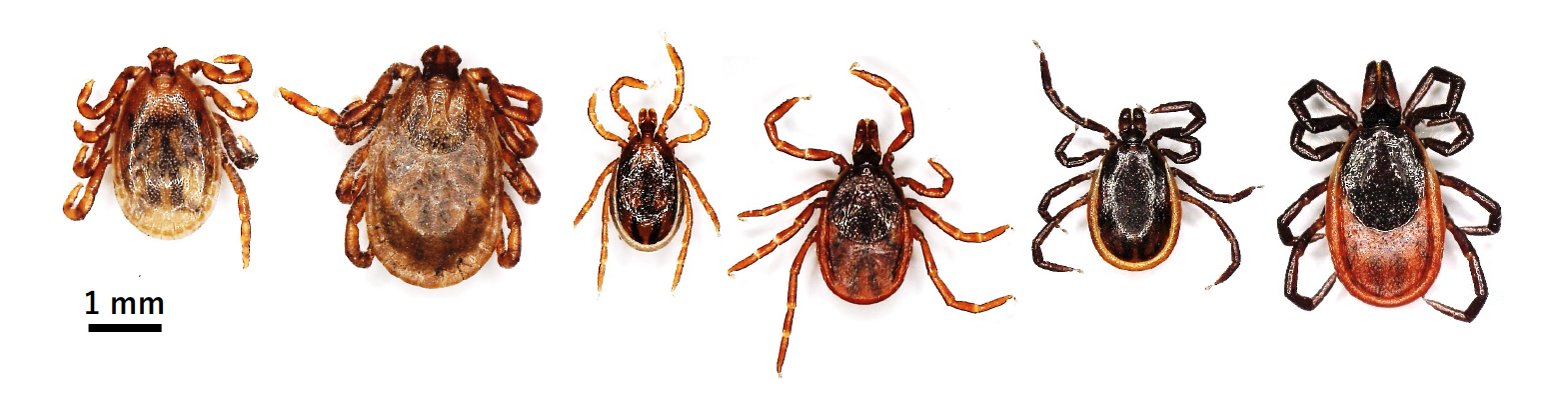

Three major species of ticks distribute in Hokkaido, Japan. From left, Haemaphysalis megaspinosa male and female, Ixodes ovatus male and female, and Ixodes persulcatus male and female. Photo: Dr. Ryo Nakao (Laboratory of Parasitology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Hokkaido University)
As the Covid-19 pandemic so dramatically demonstrates, animals carry many unknown viruses and some of these can go on to infect people. “All of the cases of Yezo virus infection we know of so far did not turn into fatalities, but it’s very likely that the disease is found beyond Hokkaido, so we need to urgently investigate its spread,” said Matsuno.
The research team now plans to track the possible nationwide distribution of the novel virus in wild animals and patients. And they say more hospitals should test for the virus in patients who complain of the symptoms.
The study was carried out in collaboration with researchers at the Graduate School of Veterinary Medicine and One Health Research Center of Hokkaido University, Sapporo City General Hospital, Nagaoka Red Cross Hospital, Hokkaido Institute of Public Health, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Nagasaki University, Rakuno Gakuen University, Health Sciences University of Hokkaido, and the University of Liverpool.
Original article:
Fumihiro Kodama, Keita Matsuno, et al., A novel nairovirus associated with acute febrile illness in Hokkaido, Japan. Nature Communications, September 20, 2021.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25857-0
Funding:
This study was supported by the World-leading Innovative and Smart Education (WISE) Program from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT); the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)/MEXT (JP16H06429, JP16H06431, JP16K21723, JP17KT0045, JP19H03112, JP20K18917, JP17H03910); Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (JP19fm0108008, JP21wm0125008, JP21fk0108081); Japan Science and Technology Agency Moonshot R&D (JPMJMS2025); Akiyama life science foundation; and the United Kingdom Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BB/P024270/1).
Contacts:
Keita Matsuno, Ph.D.
Division of Risk Analysis and Management,
International Institute for Zoonosis Control,
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81 11 706 9495
Email: matsuk[at]czc.hokudai.ac.jp
Naoki Namba (Media Officer)
Institute for International Collaboration
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2185
Email: en-press[at]general.hokudai.ac.jp

