Involvement of (Pro)renin receptor in glucose metabolism of the retina
Research Press Release | April 15, 2015
| Press Release | ||
|---|---|---|
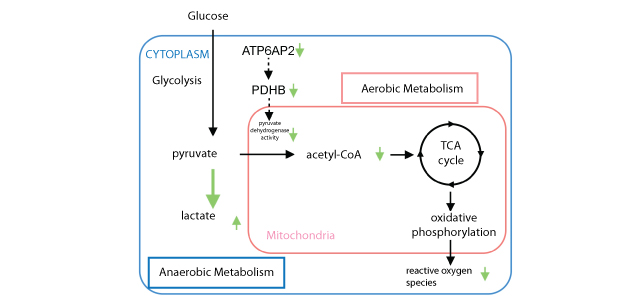
| Key Points | ・We identified the novel function of (pro)renin receptor as a pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 ß subunit (PDHB) stabilizer, contributing to aerobic glucose metabolism together with oxidative stress in the retina. | |
| Overview |
A research team of Professor Susumu Ishida and Specially Appointed Lecturer Atsuhiro Kanda, previously identified the (pro)renin receptor as an important key molecule associated the pathogenesis of end-organ damage, such as inflammation and angiogenesis, including diabetic retinopathy which leads to blindness. Research in new pharmacological therapies that target the (pro)renin receptor from various perspectives is now underway, but the physiological functions of the (pro)renin receptor in the adult retina is still not clearly unknown. In this study the tream identified the involvement of the (pro)renin receptor in glucose metabolism and reactive oxygen species production in the retina. Identifying the physiological function of the (pro)renin receptor in the retina is expected to greatly contribute to future research in drug discovery by expanding knowledge of applicable diseases and increasing knowledge of unpredicted side effects. This study was carried out under “The Matching Program for Innovations in Future Drug Discovery and Medical Care” (Hokkaido University) of the Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas Program of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. |
|
| Inquiries |
Coordinating Office, Future Drug Discovery and Medical Care Innovation Project , Hokkaido University |
|
|
Japanese Link |
(プロ)レニン受容体が網膜においてグルコース代謝に関与 -将来の有望な治療戦略の立案に貢献- | |
| Publications | ATP6AP2/(pro)renin receptor contributes to glucose metabolism via stabilizing the pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 β subunit, Journal of Biological Chemistry (2015.2.26) | |
