Lysosomal Interaction of Akt with Phafin2: A Critical Step in the Induction of Autophagy
Research Press Release | January 15, 2014
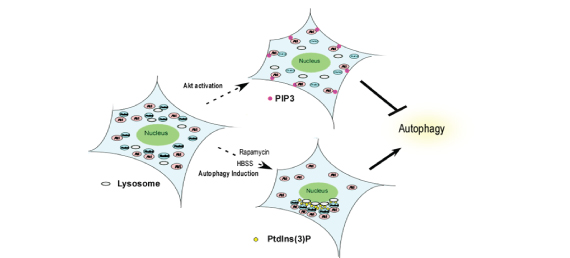
PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway is suggested to play an important role in the regulation of autophagy. However, knowledge is limited as to how Akt, a core intracellular survival regulator underlying various human cancers, controls induction of autophagy. Demonstration of the Akt-Phafin2 complexes to translocate to lysosome is essential for induction of autophagy underscore the significance of Akt in the regulation of autophagy in mammalian cells.
| Press Release | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Key Points |
We demonstrated that lysosomal accumulation of Akt and Phafin2 is a critical step in the induction of autophagy via an interaction with PtdIns (3)P. |
|
| Overview |
Using a yeast two-hybrid screen, Phafin2 (EAPF or PLEKHF2), a lysosomal protein with a unique structure of N-terminal PH (pleckstrin homology) domain and C-terminal FYVE (Fab 1, YOTB, Vac 1, and EEA1) domain was found to interact with Akt. A sucrose gradient fractionation experiment revealed that both Akt and Phafin2 co-existed in the same lysosome enriched fraction after autophagy induction. Confocal microscopic analysis and BiFC analysis demonstrated that both Akt and Phafin2 accumulate in the lysosome after induction of autophagy. BiFC analysis using PtdIns (3)P interaction defective mutant of Phafin2 demonstrated that lysosomal accumulation of the Akt-Phafin2 complex and subsequent induction of autophagy were lysosomal PtdIns (3)P dependent events. Furthermore, in murine macrophages, both Akt and Phafin2 were required for digestion of fluorescent bacteria and/or LPS-induced autophagy. Taken together, these findings establish that lysosomal accumulation of Akt and Phafin2 is a critical step in the induction of autophagy via an interaction with PtdIns (3)P. |
|
| Inquiries |
Masayuki Noguchi, Professor, Division of Cancer Biology, Institute for Genetic Medicine Hokkaido University FAX: +81-11-706-7826 |
|
|
Japanese Link |
||
| Publications | PLOS ONE | |