Molecular mechanism for antigen-presenting capacity acquisition by human gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) is clarified
Research Press Release | May 18, 2015
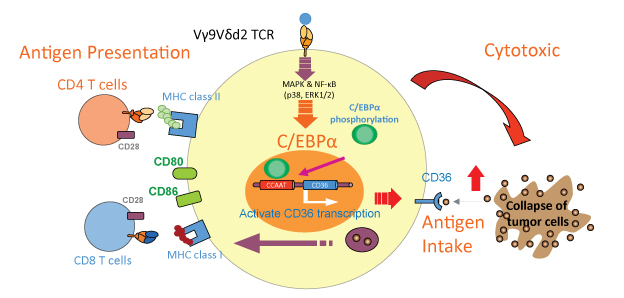
The gamma delta T cell (γδ T cell, center) expresses the CD36 scavenger receptor and takes in the antigen as it injures the tumor cell at right. During gamma delta T cell (γδ T cell) activation, the C/EBP alpha (C/EBPα) transcription factor along with signaling pathways such as p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB (NF-κB) go to work, enhancing the expression of molecules important for antigen presentation on the left.
| Press Release | ||
|---|---|---|
| Key Points | ・We discovered that human lymphocyte gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) both kill tumor cells and present tumor antigens.
・Gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) have molecular features of myeloid cells and are important for antigen-presenting capacity. ・We clarified the importance of the p38 MAPK-NF-kappaB (NF-κB) when gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) have antigen-presenting capacity. |
|
| Overview | Human lymphocytes contain various kinds of cells. One of these is gamma delta cells, which are known to play an important role in eliminating virally infected cells and tumor cells. Gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) also have an antigen-presenting capacity (the ability to tell their own T cells and other cells about foreign material) when activated, like that of dendritic cells. However, this molecular mechanism was not fully understood. Using human gamma delta cells, our research team found that these cells not only kill their opponents when mixed with tumor cells, but also take in those antigens and induce antigen-specific T cells (playing the soldier role). We also clarified that gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) express high rates of the C/EBP alpha (C/EBPα) transcription factor, which is typically high in myeloid cells, and the CD36 scavenger receptor, which works in the uptake of dead cell debris and other material, and that gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) use the p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB (NF-κB) signaling pathways when presenting antigens to T cells. These findings will serve as basic knowledge in the development of new therapies for tumor immunity. | |
| Inquiries |
Ken-ichiro Seino, Professor, Division of Immunobiology, Institute for Genetic Medicine, Hokkaido University TEL: +81-11-706-5531 FAX: +81-11-706-7545 E-mail: seino@igm.hokudai.ac.jp |
|
|
Japanese Link |
ヒトガンマデルタ T 細胞による抗原提示能獲得の分子メカニズムを解明 | |
| Publications | Myeloid molecular characteristics of human γδ T cells support their acquisition of tumor antigen-presenting capacity, Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2015.4.24) | |
