Natural defense mechanism preventing cancer at the earliest stage
Research Press Release | May 15, 2017
A new study shows cells in the initial stage of cancer change their metabolism before getting eliminated by the surrounding normal cells, providing a novel target for developing cancer prevention drugs.
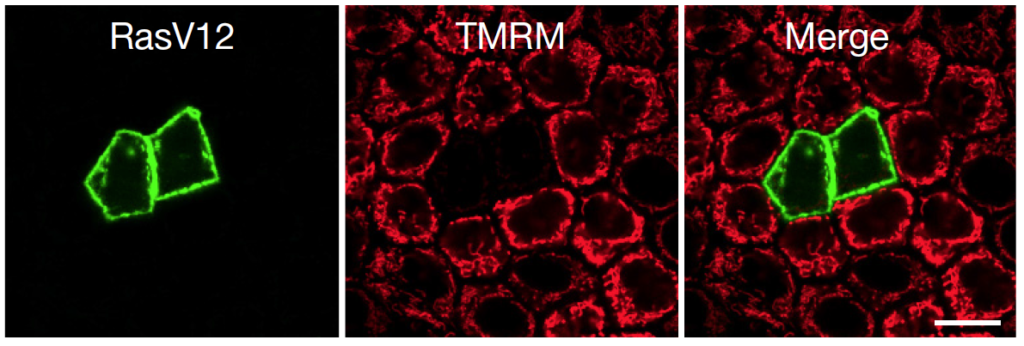
Most cancers begin when one or more genes in a cell mutate. These newly “transformed” cells get extruded and eliminated after losing a competition against the surrounding normal cells in the epithelium, or the outer layer of the body. However, the mechanism by which normal cells recognize and attack the transformed cells remains elusive.
A research team led by Professor Yasuyuki Fujita of Hokkaido University’s Institute for Genetic Medicine explored this natural defense mechanism using cultured mammalian cells and a mouse model. The study uncovered two metabolic changes occurring in the newly transformed cells: mitochondrial dysfunction and an elevated glucose uptake. The changes were significant only when the transformed cells were surrounded by normal epithelial cells, indicating that the changes are induced by the normal cells. Furthermore, according to the study, the metabolic changes play an important role in eliminating the transformed cells.
Interestingly, these metabolic changes are similar to the Warburg effect, which is observed in cancerous cells in the middle and latter stages of cancer. The Warburg effect is generally thought to play tumor promoting roles whereas the newly discovered metabolic changes could suppress cancer in its initial stage. “Although these two processes have similar metabolic alterations, mitochondrial downregulation and increased glycolysis, they are governed by distinct regulators and have opposing effects on the development of cancer,” says Fujita.
Their findings shed new light on the inherent ability of normal cells to eliminate cancerous cells and opens up potential avenues for cancer prevention. “Considering that the metabolic changes could either suppress or promote cancer cells depending on the stage, further elucidation of the mechanism is essential to help develop cancer prevention drugs while avoiding adverse effects,” Fujita commented.
This research was conducted by scientists from Hokkaido University, Kyoto University, Kanazawa University, Keio University, Osaka University and University College London, and published in the May issue of Nature Cell Biology. The paper is also featured in the “News and Views” section of the issue.
Original article:
Kon S., et al., Cell competition with normal epithelial cells promotes apical extrusion of transformed cells through metabolic changes, Nature Cell Biology, April 17, 2017.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3509
Funding information:
This research is supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas 26114001 and 26112701, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) 26250026 and the AMED Strategic Japanese–Swiss Cooperative Program, Takeda Science Foundation, the Kato Memorial Bioscience Foundation and The YASUDA Medical Foundation.
Contacts:
Professor Yasuyuki Fujita
Institute for Genetic Medicine
Hokkaido University
Email: yasu[at]igm.hokudai.ac.jp
Naoki Namba (Media Officer)
Global Relations Office
Institute for International Collaboration
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2185
Email: pr[at]oia.hokudai.ac.jp