The molecules that energize babies’ hearts
Research Press Release | June 14, 2018
A metabolic process that provides heart muscle with energy fails to mature in newborns with thickened heart walls, according to a Japan–Canada research team.
Hokkaido University cardiologist Arata Fukushima, along with a team of University of Alberta scientists led by Gary Lopaschuk, examined the heart tissue of 84 newborns who had undergone surgery for congenital heart disease. Many patients with the disease develop thickened heart walls, or hypertrophy, which can lead to fatal heart failure even after the surgery.
Before birth, cardiac muscle cells use energy generated by breaking down glucose. Immediately after birth, they rapidly switch to breaking down fatty acids. This switch is hindered in hypertrophied newborn hearts. Fukushima and his team wanted to investigate how this happens at the molecular level.
In the study, published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight, the team compared the biopsy samples taken from normal and thickened right ventricular walls. They found that two enzymes involved in fatty acid break down, called LCAD and βHAD, were “hyperacetylated” in non-hypertrophied right ventricles. This means that large amounts of acetyl groups were added to the enzyme proteins, increasing their activity levels. This, in turn, led to increased fatty acid metabolism.
In hypertrophied hearts, these two enzymes were not hyperacetylated, leading to reduced fatty acid metabolism in these newborns. The team detected reduced activity of an acetylation promoting gene, called gcn5l1, in hypertrophied hearts.
When the team experimented on cultured hypertrophy-like cardiac muscle cells, they found that turning off the gcn5l1 gene led to decreased acetylation of LCAD and βHAD, and a reduced fatty acid oxidation in the cells. Moreover, the cells lacking gcn5l1 formed thicker muscle fibers comparing to normal cells.
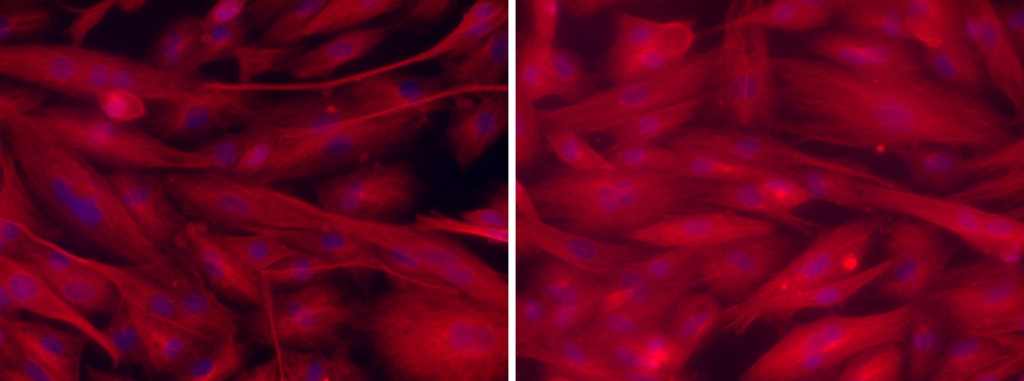
The cultured cells lacking gcn5l1(right) formed thicker muscle fibers comparing to normal cells (left). (Fukushima A. et al., The Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight, May 17, 2018)
“Our findings show that acetylation of metabolic enzymes plays an important role in controlling the dramatic changes in energy metabolism that occur in newborn hearts immediately after birth,” says Arata Fukushima. “The findings also show how hypertrophy can perturb this process by delaying the maturation of fatty acid metabolism, which compromises the ability of the newborn heart to generate energy. Developing drugs that enhance acetylation of the metabolic enzymes could help treat patients with hypertrophy.”
Original article:
Fukushima A. et al., Acetylation contributes to hypertrophy caused maturational delay of cardiac energy metabolism. The Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight, May 17, 2018.
DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.99239
Contacts:
Assistant Professor Arata Fukushima
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine
Graduate School of Medicine
Hokkaido University
Email: arating77[at]huhp.hokudai.ac.jp
Naoki Namba (Media Officer)
Global Relations Office
Institute for International Collaboration
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2185
Email: pr[at]oia.hokudai.ac.jp