Turkestan cockroach selling online is a companion of the common household cockroach
Research Press Release | July 19, 2019
The Turkestan cockroach (commonly known as the red runner roach or rusty red roach), which is popular as food for pet reptiles, has an interneuron extremely sensitive to sex pheromones emitted by American cockroaches, providing evidence that the Turkestan cockroach is phylogenetically close to the American cockroach and the smoky brown cockroach belonging to the genus Periplaneta.
Many nocturnal animals including insects use a species-specific smell, that is sex a pheromone, to locate and attract potential mates. For example, female American cockroaches emit sex pheromones called “periplanones” with unique chemical structures. Males that detect them with their antennae orientate towards the pheromone source, preform courtship rituals, and mate.
The Turkestan cockroach, Blatta lateralis, also known as red cockroach, has now growing attention as a world-wide invasive pest, especially in the southern United States. Its origin is temperate to subtropical zones of the Middle East. “The Turkestan cockroach is popular as live food among reptile breeders and can be easily purchased online. So, this would be the first species that expands its habitat via the internet,” says Hiroshi Nishino of Hokkaido University.
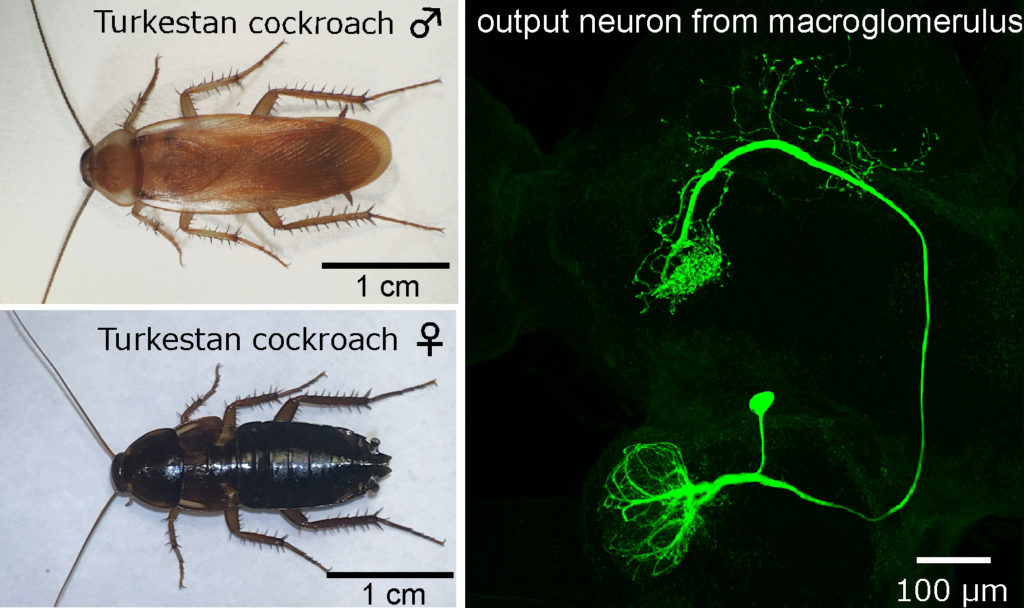
A male and female Turkestan cockroach (left panels), and an output neuron from its enlarged glomerulus (right panel). (Domae M., et al., Neuroscience Letters, June 8, 2019)
Recent molecular genetic studies have shown that the Turkestan cockroach is phylogenetically close to the American cockroach in the genus Periplaneta, despite their morphological and habitational differences.
This study, led by Hiroshi Nishino and published in Neuroscience Letters, found that the Turkestan cockroach uses periplanones or similar substances as sex pheromones. The experiments showed a male Turkestan cockroach has an extremely large glomerulus that specifically processes sex pheromones in a part of the brain called the antennal lobe. The glomerulus was three times bigger than that of American cockroaches, suggesting it has more sensory cells for processing sex pheromones. Accordingly, the output neuron from the large glomerulus was extremely sensitive to periplanones. As little as 0.1 femtograms of pheromone contained in a filter paper was sufficient to excite the output neuron when the paper contacted a very small region (approx. 1mm) of the antenna. This sensitivity to periplanone was more than 100 times higher compared to that of the American cockroach.
Researchers also found that a male Turkestan cockroach was attracted to periplanone, but, unlike American cockroaches, the pheromone alone did not trigger courtship rituals. Courtship rituals started only after coming in contact with a female of the same species. This implies that a low volatile substance on the female’s body plays an important role in preventing the species from mating with other species.
American cockroaches start courtship rituals right after the sex pheromone periplanone is presented (left). Turkestan cockroaches are attracted to the same sex pheromone but do not show a courtship display. (Domae M. et al., Neuroscience Letters, June 8, 2019)
“Turkestan cockroaches adapt to inground containers where odor molecules diffuse very slowly and this could be why they have evolved an enlarged glomerulus to detect tiny packets of pheromones,” says Hiroshi Nishino. He added, “We need exercise caution when handling Turkestan cockroaches because they are a member of the genus Periplaneta, in which most have become household pests worldwide.
Original article:
Domae M., Iwasaki M., Mizunami M. and Nishino H., Functional unification of sex pheromone-receptive glomeruli in the invasive Turkestan cockroach derived from the genus Periplaneta, Neuroscience Letters, June 8, 2019.
DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134320
Funding:
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (17K07479).
Contacts:
Assistant Professor Hiroshi Nishino
Research Institute for Electronic Science (RIES)
Hokkaido University
Email: nishino[at]es.hokudai.ac.jp
Naoki Namba (Media Officer)
Institute for International Collaboration
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2185
Email: en-press[at]general.hokudai.ac.jp
