Unraveling the mysteries of Nipponosaurus
Research Press Release | June 09, 2017
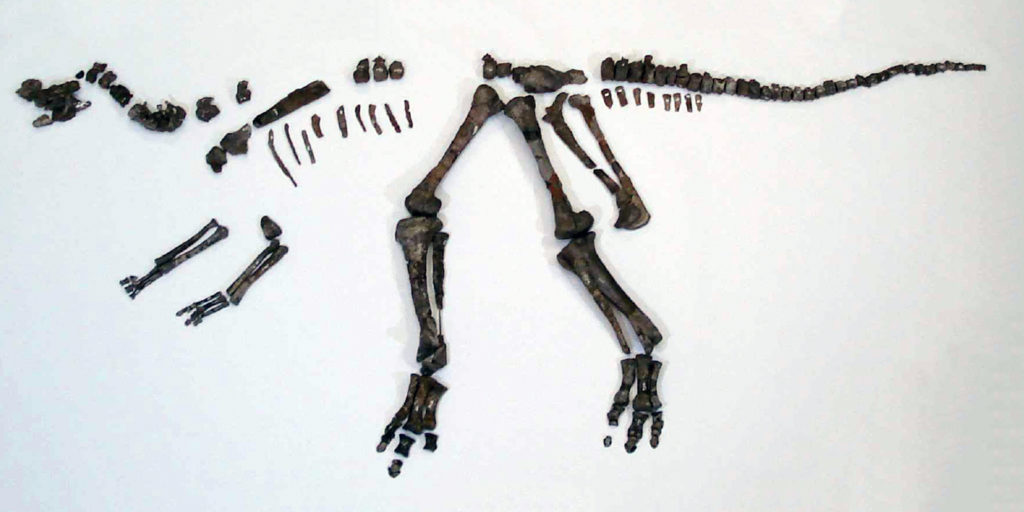
Nipponosaurus sachalinensis – a controversial hadrosaurid dinosaur whose fossilized skeleton was unearthed in southern Sakhalin in 1934 – is found to be a valid taxon and a juvenile that had not reached sexual maturity.
Nipponosaurus, a herbivorous dinosaur of the Late Cretaceous Period, was named so in 1936 by Professor Takumi Nagao of Hokkaido Imperial University (predecessor of Hokkaido University). The name refers to the Japanese word for Japan (Nippon), as Southern Sakhalin was Japan’s territory before World War II. It was the first study of dinosaurs in Japan and Nagao’s work is considered as the genesis of Japan’s dinosaur research.
In 2004, a reanalysis of the dinosaur by a graduate student of Hokkaido University revealed that Nipponosaurus was a juvenile and closely related to the North American hadrosaurid Hypacrosaurus. Since then, several conflicting hypotheses were proposed, including some denying an independent taxonomic status of Nipponosaurus. This theory stemmed from the fact that the fossilized bones came from an immature dinosaur, so its bones would have changed as it grew older.
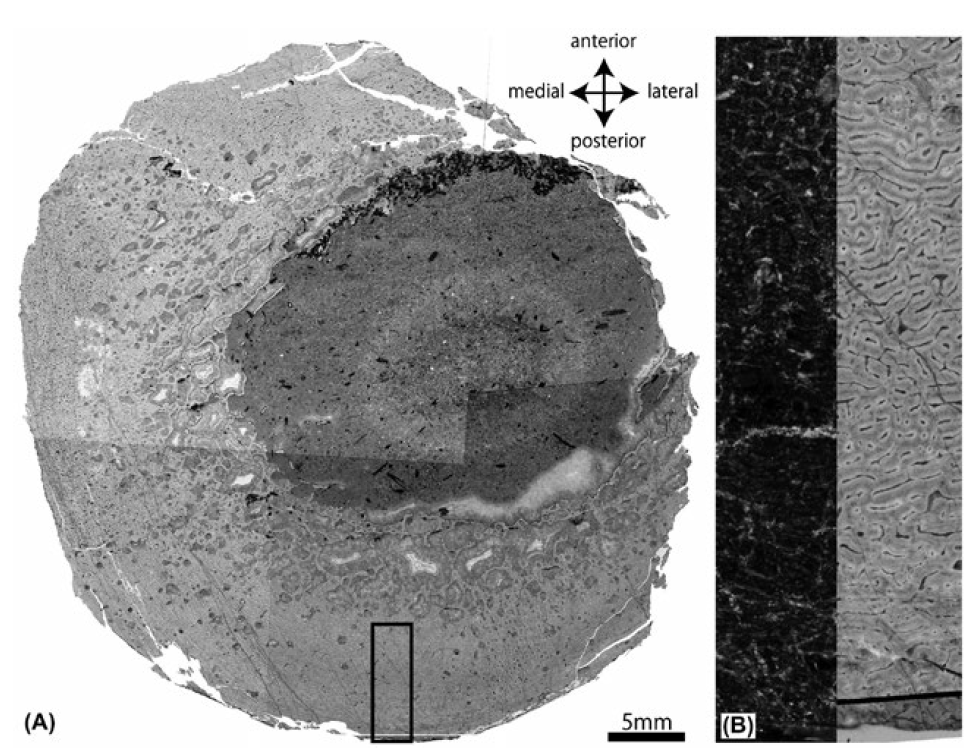
Ryuji Takasaki, a graduate student of Hokkaido University, associate Professor Yoshitsugu Kobayashi at the Hokkaido University Museum and their collaborators in Canada and the U.S. investigated the developmental stage of the Nipponosaurus by dissecting three fossilized bones (a femur, rib and chevron). They found the orientation of vascular canals in the thighbone change from reticular in the inner cortex to laminar in the outer cortex. They also figured out that the number of lines indicating arrested growth, similar to growth rings in a tree, is limited to two in all bones. Both of these features are showing that Nipponosaurus was a juvenile yet to reach sexual maturity.
The researchers also investigated the bones of hadrosaurids in each developmental stage up to adulthood to examine how the bones transformed as they grew. Some bones did not change their form through these stages.
By comparing the bones of Nipponosaurus and other hadrosaurids, the team discovered unique characteristics within the bones of Nipponosaurus that should not change as it develops. This finding led to the conclusion that Nipponosaurus is indeed a valid taxon. The unique characteristics are a wide shelf-like structure on the lower jaw, coronoid process stretching vertically from the shelf-like structure, and extremely short front legs.
The researchers concluded Nipponosaurus is a more primitive hadrosaurid than previously thought and closely related to Europe’s hadrosaurid Blasisaurus and Arenysaurus, indicating Nipponosaurus is one of the dinosaur species that migrated from Europe, not North America, to the Far East.
“Our study clarified the phylogenetic status of Nipponosaurus, and we are now interested in the relationship between Nipponosaurus and other Japanese dinosaurs, whose fossils have been unearthed one after another in recent years. We aim to discover how diverse dinosaurs inhabited East Asian coastal areas,” says Ryuji Takasaki.
Original article:
Takasaki R., et al., Reanalysis of the phylogenetic status of Nipponosaurus sachalinensis (Ornithopoda: Dinosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of southern Sakhalin, Historical Biology, May 5, 2017.
DOI: 10.1080/08912963.2017.1317766
Contacts:
Associate Professor Yoshitsugu Kobayashi
The Hokkaido University Museum
Email: ykobayashi[at]museum.hokudai.ac.jp
Naoki Namba (Media Officer)
Global Relations Office
Institute for International Collaboration
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2185
Email: pr[at]oia.hokudai.ac.jp