Deep-sea black carbon comes from hydrothermal vents
Joint release by Hokkaido University and Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, the University of Tokyo.
Hydrothermal vents have been identified as a previously undiscovered source of dissolved black carbon in the oceans, furthering the understanding of the role of oceans as a carbon sink.

The ocean is one of the largest dynamic carbon sinks in the world, and is susceptible to increased carbon emissions from human activities. There are even proposals to use the ocean to sequester carbon in an effort to reduce the carbon emissions. However, much of the processes by which the ocean functions as a carbon sink are not fully understood.
Associate Professor Youhei Yamashita and grad student Yutaro Mori at Hokkaido University, along with Professor Hiroshi Ogawa at AORI, The University of Tokyo, have revealed conclusive evidence that hydrothermal vents are a previously unknown source of dissolved black carbon in the deep ocean. Their discoveries were published in the journal Science Advances.
“One of the largest carbon pools on the Earth’s surface is the dissolved organic carbon in the ocean,” explains Ogawa. “We were interested in a portion of this pool, known as dissolved black carbon (DBC), which cannot be utilized by organisms. The source of DBC in the deep sea was unknown, although hydrothermal vents were suspected to be involved.”
The researchers analyzed the distribution of DBC in the ocean basins of the North Pacific Ocean and Eastern South Pacific Ocean, and compared the data with previously reported concentrations of a helium isotope that is associated with hydrothermal vent emissions, as well as oxygen utilization in these areas.
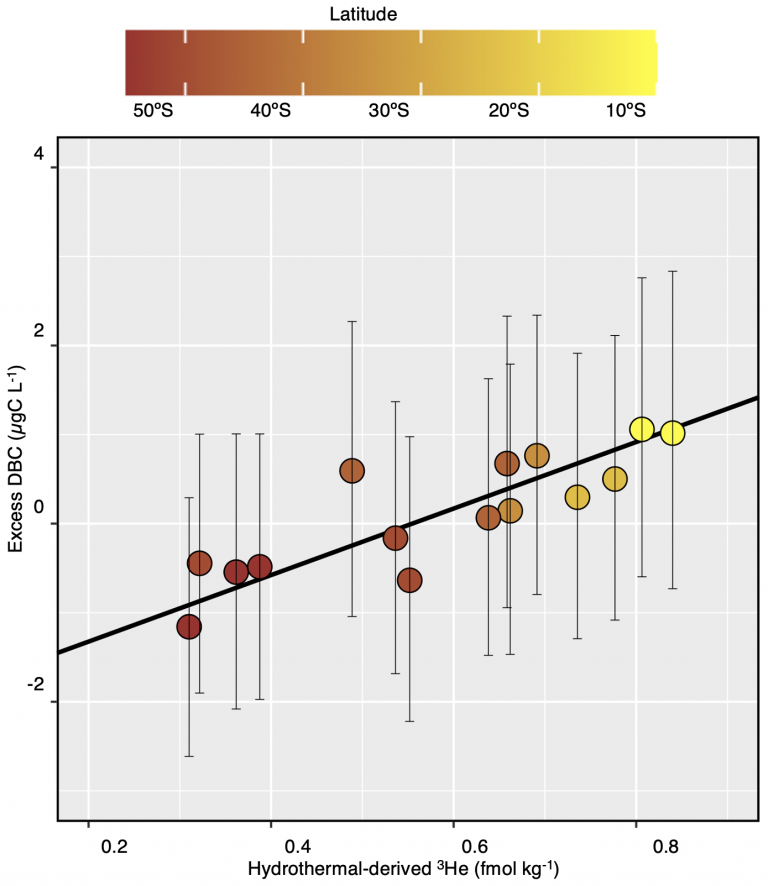
Their findings showed that hydrothermal vents were an important source of DBC in the Pacific Ocean. This hydrothermal DBC is most likely formed due to the mixing of the hot fluids from hydrothermal vents with cold seawater, and is transported over long distances — up to thousands of kilometers away.
“Most importantly, our research indicates that the DBC from hydrothermal vents is an important source of dissolved organic carbon in the deep ocean. In terms of DBC inputs to the ocean, hydrothermal vents may contribute up to half as much DBC as that which is formed by biomass burning or fossil fuel combustion and subsequently transported via rivers or atmospheric deposition,” concluded Yamashita. Further research is required to understand exactly how DBC is formed from hydrothermal vents.
Original Article:
Youhei Yamashita, Yutaro Mori, Hiroshi Ogawa. Hydrothermal-derived black carbon as a source of recalcitrant dissolved organic carbon in the ocean. Science Advances. February 9, 2023.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade3807
Funding:
This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) grants KAKENHI (JP16H02930, JP19H04249, JP22H03714, JP19H05667, JP19H04260).
Contacts:
Associate Professor Youhei Yamashita
Faculty of Environmental Earth Science,
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2349
Email: yamashiy[at]ees.hokudai.ac.jp
Professor Hiroshi Ogawa
Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute (AORI)
The University of Tokyo
Tel: +81-47-136-6091
Email: hogawa[at]aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Sohail Keegan Pinto (International Public Relations Specialist)
Public Relations Division
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2186
Email: en-press[at]general.hokudai.ac.jp
Public Relations Office
Center for Cooperative Research Promotion
Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute
The University of Tokyo
Email: kouhou[at]aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp
